INTERNACIONAL
UN revisits ‘killer robot’ regulations as concerns about AI-controlled weapons grow

Several nations met at the United Nations (U.N.) on Monday to revisit a topic that the international body has been discussing for over a decade: the lack of regulations on lethal autonomous weapons systems (LAWS), often referred to as «killer robots.»
This latest round of talks comes as wars rage in Ukraine and Gaza.
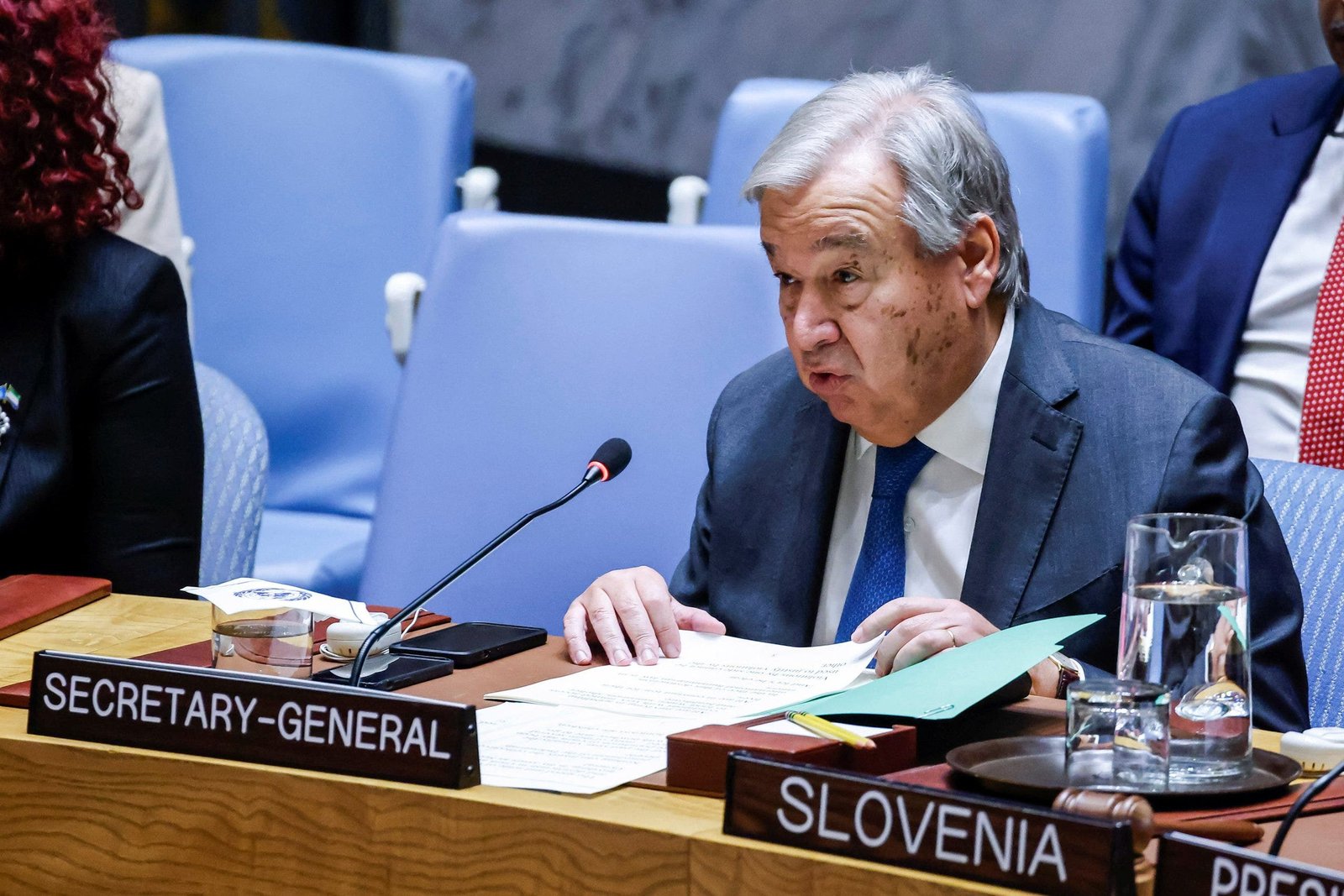
While the meeting was held behind closed doors, U.N. Secretary-General António Guterres released a statement doubling down on his 2026 deadline for a legally binding solution to threats posed by LAWS.
«Machines that have the power and discretion to take human lives without human control are politically unacceptable, morally repugnant and should be banned by international law,» Guterres said in a statement. «We cannot delegate life-or-death decisions to machines,» he later added.
United Nations Secretary-General António Guterres speaks during a Security Council meeting during the 79th United Nations General Assembly at U.N. headquarters in New York City on Sept. 27, 2024. (Reuters/Eduardo Munoz)
FORMER TRUMP OFFICIAL SLAMS UN REFORM EFFORTS AS ‘EIGHT AND A HALF YEARS LATE’
International Committee of the Red Cross (ICRC) President Mirjana Spoljaric delivered a statement to nations participating in Monday’s meeting. Spoljaric expressed the ICRC’s support for efforts to regulate LAWS but warned that technology is evolving faster than regulations, making threats posed by the systems «more worrying.»
«Machines with the power and discretion to take lives without human involvement threaten to transform warfare in ways with grave humanitarian consequences. They also raise fundamental ethical and human rights concerns. All humanity will be affected,» Spoljaric said.
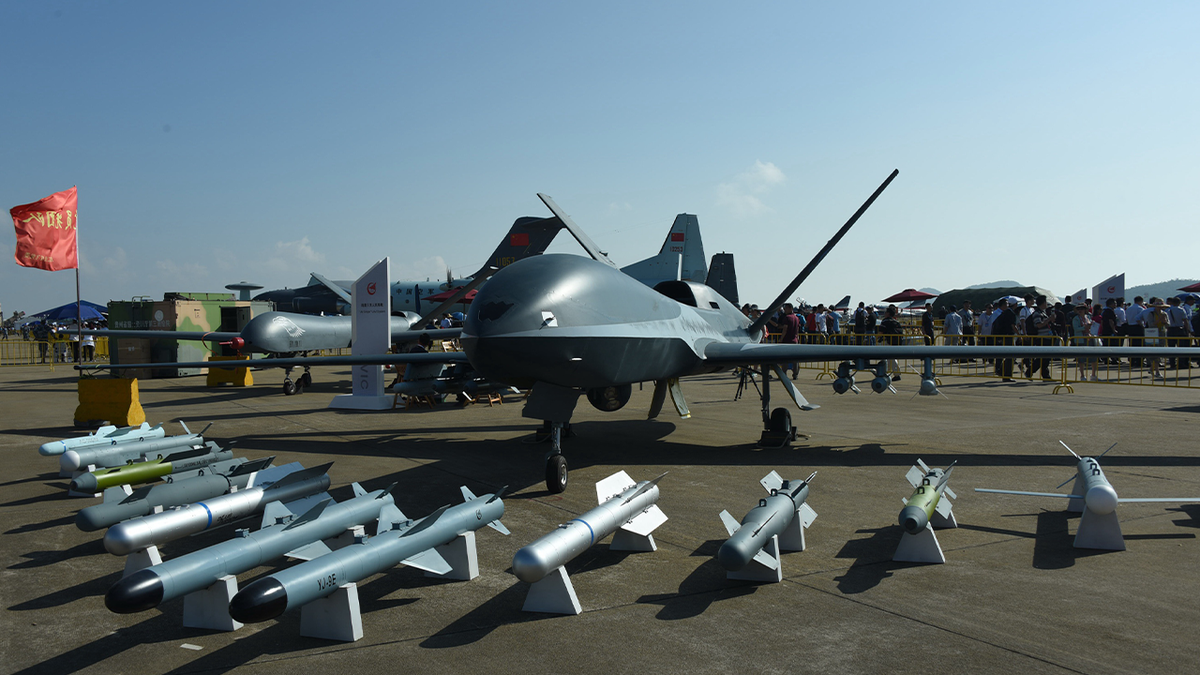

The picture shows the unmanned aerial vehicle of China captured at the Zhuhai Air Show on Nov. 7, 2018. (Costfoto/Future Publishing via Getty Images)
NUCLEAR WATCHDOG URGES ‘TRUST BUT VERIFY’ THAT IRAN ENGAGES IN GOOD-FAITH NEGOTIATIONS
Artificial intelligence is not necessarily a prerequisite for something to be considered an autonomous weapon, according to the U.N., as not all autonomous systems fully rely on AI. Some can use pre-programmed functions for certain tasks. However, AI «could further enable» autonomous weapons systems, the U.N. said.
Vice President of the Conservative Partnership Institute Rachel Bovard, however, says that while regulation of autonomous weapons is necessary, the U.S. needs to be cautious when it comes to the development of international law.
«AI is the wild west and every country is trying to determine the rules of the road. Some regulation will be imperative to preserving our humanity. When it comes to international law, however, the U.S. should proceed with caution,» Bovard told Fox News Digital. «As we have learned with everything from trade to health, subjecting our national sovereignty to international dictates can have lasting unintended consequences. If existing international law is sufficient at the moment, that is what should govern.»

Palestinian President Mahmoud Abbas addresses the 79th session of the United Nations General Assembly on Thursday, Sept. 26, 2024 at U.N. headquarters. (AP Photo/Frank Franklin II)
CLICK HERE TO GET THE FOX NEWS APP
Countries in the Convention on Certain Conventional Weapons have been meeting since 2014 to discuss a possible full ban on LAWS that operate without human control and to regulate those with more human involvement, according to Reuters.
In 2023, more than 160 nations backed a U.N. resolution calling on countries across the globe to address the risks posed by LAWS. However, there is currently no international law specifically regulating LAWS.
INTERNACIONAL
Russia sat on intel of Hillary Clinton’s alleged ‘heavy tranquilizers’ use, new docs claim

NEWYou can now listen to Fox News articles!
Russia allegedly had intelligence suggesting that former Secretary of State Hillary Clinton was taking «heavy tranquilizers,» which former President Barack Obama and Democratic Party leaders found to be «extraordinarily alarming,» a newly declassified intelligence report claims.
Fox News Digital first reported that the U.S. intelligence community did not have any direct information that Russian President Vladimir Putin wanted to help elect Donald Trump during the 2016 election, but, at the «unusual» direction of then-President Obama, reportedly published «potentially biased» or «implausible» intelligence suggesting otherwise.
BRENNAN DIRECTED PUBLICATION OF ‘IMPLAUSIBLE’ REPORTS CLAIMING PUTIN PREFERRED TRUMP IN 2016, HOUSE FOUND
The information came from a report declassified by Director of National Intelligence Tulsi Gabbard. The report was prepared by the House Permanent Select Committee on Intelligence in 2020.
The report, which was based on an investigation launched by former House Intelligence Committee Chairman Devin Nunes, R-Calif., was dated Sept. 18, 2020. At the time of the publication of the report, Rep. Adam Schiff, D-Calif., was the chairman of the committee.
The report had never before been released to the public, and instead, remained highly classified within the intelligence community.
Fox News Digital obtained the «fully-sourced limited-access investigation report that was drafted and stored in a limited-access vault at CIA Headquarters.» The report includes some redactions.
One section of the report states that the material in Putin’s possession included Russian intelligence on Democratic National Committee information allegedly showing that senior Democrat leaders found Clinton’s health to be «extraordinarily alarming.»
Then-President Obama stands with then-Secretary of State Hillary Clinton. (AP)
«As of September 2016, the Russian Foreign Intelligence Service had DNC information that President Obama and Party leaders found the state of Secretary Clinton’s health to be ‘extraordinarily alarming,’ and felt it could have ‘serious negative impact’ on her election prospects,» the report states. «Her health information was being kept in ‘strictest secrecy’ and even close advisors were not being fully informed.»
The Russian Foreign Intelligence Service also allegedly had DNC communications that showed that «Clinton was suffering from ‘intensified psycho-emotional problems, including uncontrolled fits of anger, aggression, and cheerfulness.’»
«Clinton was placed on a daily regimen of ‘heavy tranquilizers’ and while afraid of losing, she remained ‘obsessed with a thirst for power,’» the report states.
The Russians also allegedly had information that Clinton «suffered from ‘Type 2 diabetes, Ischemic heart disease, deep vein thrombosis, and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease.’»
The Russians also allegedly possessed a «campaign email discussing a plan approved by Secretary Clinton to link Putin and Russian hackers to candidate Trump in order to ‘distract the American public’ from the Clinton email server scandal.»
Gabbard, during the White House press briefing Wednesday, said there were «high level DNC emails that detailed evidence of Hillary’s, quote, psycho-emotional problems, uncontrolled fits of anger, aggression and cheerfulness, and that then Secretary Clinton was allegedly on a daily regimen of heavy tranquilizers.»
«Then CIA Director Brennan and the intelligence community mischaracterized intelligence and relied on dubious, substandard sources to create a contrived false narrative that Putin developed a, quote unquote, ‘clear preference’ for Trump,» Gabbard said. «Brennan and the IC misled lawmakers by referencing the debunked Steele dossier to assess, quote unquote, ‘Russia’s plans and intentions,’ falsely suggesting that this dossier had intelligence value when he knew that it was discredited, the intelligence community excluded significant intelligence and ignored or selectively quoted reliable intelligence that contradicted the intelligence community assessments.»
«Key findings on Putin’s alleged support for Trump, including this intelligence reporting, would have exposed the ICA’s claim as implausible, if not ridiculous,» she said.
Neither Clinton nor Obama responded to Fox News Digital’s request for comment.
A tranquilizer is a drug used to reduce mental disturbance, such as anxiety and tension. Tranquilizers are typically prescribed to individuals suffering from anxiety, sleep disturbances and related conditions affecting their mental and physical health.
OBAMA OFFICIALS ADMITTED THEY HAD NO ‘EMPIRICAL EVIDENCE’ OF TRUMP-RUSSIA COLLUSION: HOUSE INTEL TRANSCRIPTS
Fox News Digital, in 2020, first reported on the «Clinton Plan.»
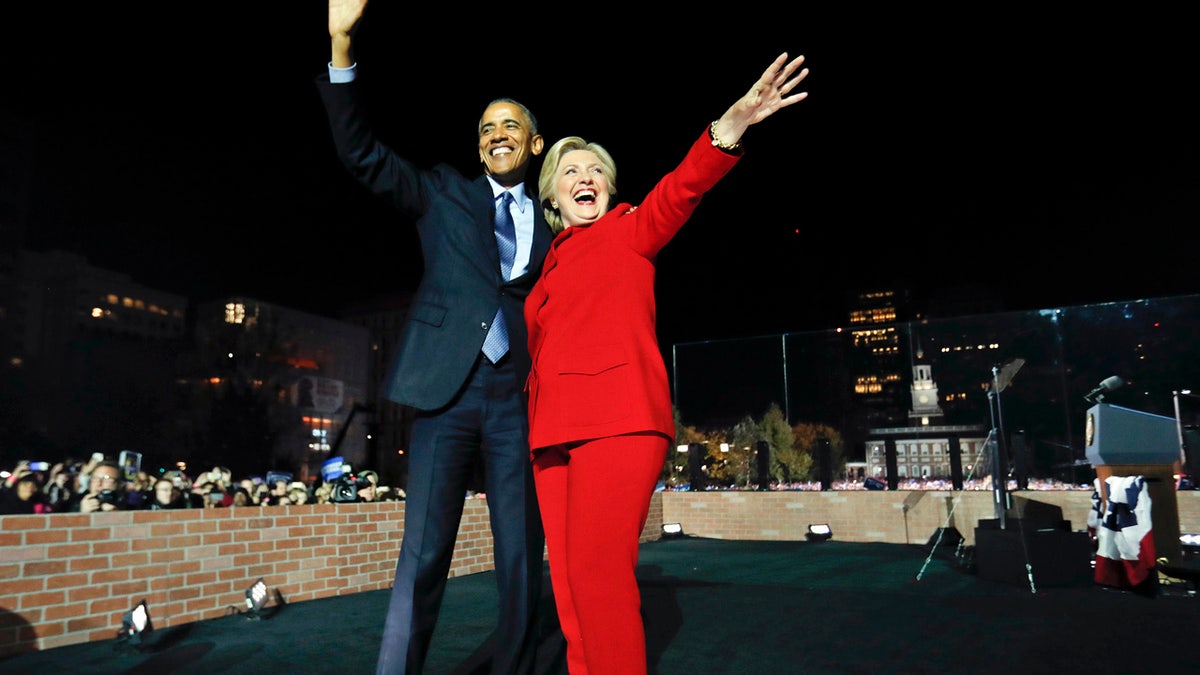

President Barack Obama waves on stage with Democratic presidential candidate Hillary Clinton during a rally at Independence Hall in Philadelphia, Nov. 7, 2016. (Pablo Martinez Monsivais/The Associated Press)
On July 28, 2016, then-CIA Director John Brennan briefed Obama on a plan from one of Clinton’s campaign foreign policy advisors allegedly «to vilify Donald Trump by stirring up a scandal claiming interference by the Russian security service.»
Comey, Vice President Joe Biden, Attorney General Loretta Lynch and Director of National Intelligence James Clapper were in the Brennan–Obama briefing.
After that briefing, the CIA reportedly properly forwarded that information through a Counterintelligence Operational Lead (CIOL) to Comey and Deputy Assistant Director of Counterintelligence Peter Strzok, with the subject line: «Crossfire Hurricane.»
Fox News Digital exclusively obtained and reported on the CIOL in October 2020, which stated: «The following information is provided for the exclusive use of your bureau for background investigative action or lead purposes as appropriate.»
«Per FBI verbal request, CIA provides the below examples of information the CROSSFIRE HURRICANE fusion cell has gleaned to date,» the memo continued. «An exchange (REDACTED) discussing US presidential candidate Hillary Clinton’s approval of a plan concerning US presidential candidate Donald Trump and Russian hackers hampering US elections as a means of distracting the public from her use of a private email server.»
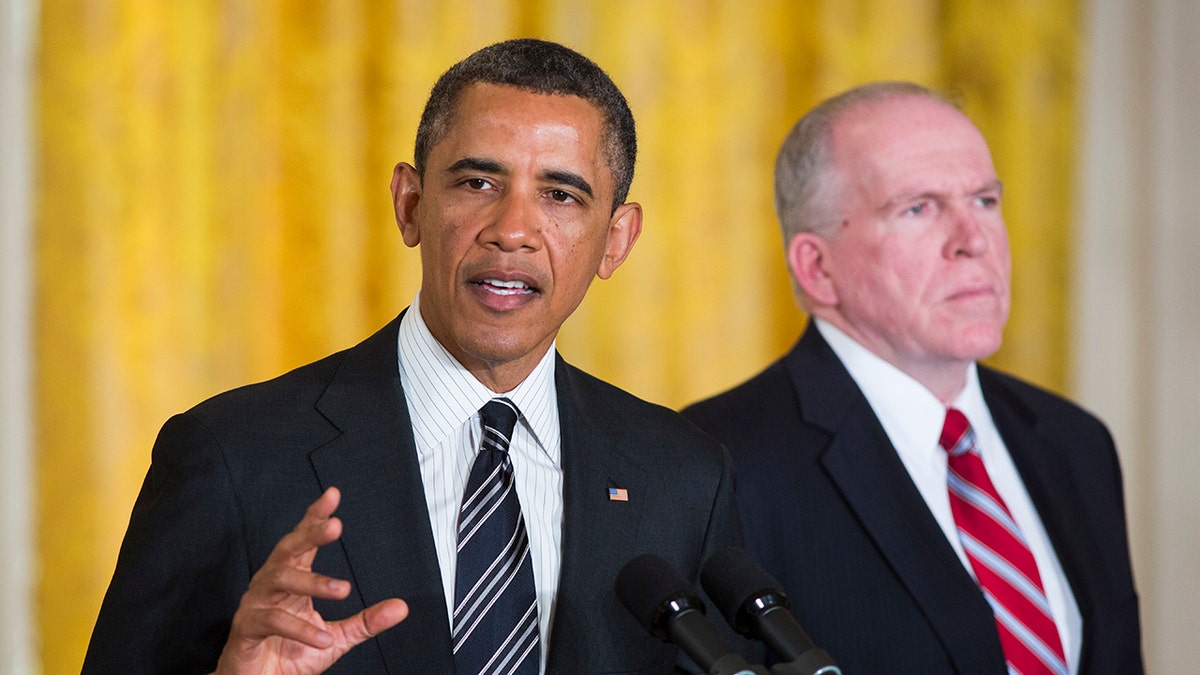

President Barack Obama in the East Room of the White House announcing he was nominating John Brennan as the new CIA director. (Brooks Kraft LLC/Corbis via Getty Images)
The FBI on July 31, 2016, opened a counterintelligence investigation into whether candidate Trump and members of his campaign were colluding or coordinating with Russia to influence the 2016 campaign. That investigation was referred to inside the bureau as «Crossfire Hurricane.»
OBAMA ADMIN ‘MANUFACTURED’ INTELLIGENCE TO CREATE 2016 RUSSIAN ELECTION INTERFERENCE NARRATIVE, DOCUMENTS SHOW
Former Special Counsel Robert Mueller was appointed to take over the FBI’s original «Crossfire Hurricane» investigation. After nearly two years, Mueller’s investigation, which concluded in March 2019, yielded no evidence of criminal conspiracy or coordination between the Trump campaign and Russian officials during the 2016 presidential election.
Shortly after, John Durham was appointed as special counsel to investigate the origins of the «Crossfire Hurricane» probe.
Durham found that the FBI «failed to act» on a «clear warning sign» that the bureau was the «target» of a Clinton-led effort to «manipulate or influence the law enforcement process for political purposes» ahead of the 2016 presidential election.

President Barack Obama speaks to the media after meeting with Attorney General Loretta Lynch and FBI Director James Comey in the Oval Office at the White House on July 19, 2016. (Mark Wilson/Getty Images)
«The aforementioned facts reflect a rather startling and inexplicable failure to adequately consider and incorporate the Clinton Plan intelligence into the FBI’s investigative decision-making in the Crossfire Hurricane investigation,» Durham’s report states.
«Indeed, had the FBI opened the Crossfire Hurricane investigation as an assessment and, in turn, gathered and analyzed data in concert with the information from the Clinton Plan intelligence, it is likely that the information received would have been examined, at a minimum, with a more critical eye,» the report continued.
Durham, in his report, said the FBI «failed to act on what should have been – when combined with other incontrovertible facts – a clear warning sign that the FBI might then be the target of an effort to manipulate or influence the law enforcement process for political purposes during the 2016 presidential election.»
Meanwhile, the report states that Brennan «ordered the post-election publication of 15 reports containing previously collected but unpublished intelligence, three of which were substandard – containing information that was unclear, of uncertain origin, potentially biased, or implausible – and those became foundational sources for the ICA judgments that Putin preferred Trump over Clinton.»
FBI LAUNCHES CRIMINAL INVESTIGATIONS OF JOHN BRENNAN, JAMES COMEY: DOJ SOURCES
«The ICA misrepresented these reports as reliable, without mentioning their significant underlying flaws,» the committee found.
«One scant, unclear, and unverifiable fragment of a sentence from one of the substandard reports constitutes the only classified information cited to suggest Putin ‘aspired’ to help Trump win,» the report states, adding that the ICA «ignored or selectively quoted reliable intelligence reports that challenged-and in some cases undermined – judgments that Putin sought to elect Trump.»
The report also states that the ICA «failed to consider plausible alternative explanations of Putin’s intentions indicated by reliable intelligence and observed Russian actions.»
The committee also found that two senior CIA officers reportedly warned Brennan that «we don’t have direct information that Putin wanted to get Trump elected.»
Despite those warnings, the Obama administration moved to publish the ICA.
The report also includes intelligence from a longtime Putin confidant who explained to investigators that «Putin told him he did not care who won the election,» and that Putin «had often outlined the weaknesses of both major candidates.»
FLASHBACK: DNI DECLASSIFIES BRENNAN NOTES, CIA MEMO ON HILLARY CLINTON ‘STIRRING UP’ SCANDAL BETWEEN TRUMP, RUSSIA
The report also stated that the ICA committed context showing that the claim that Putin preferred Trump was «implausible – if not ridiculous.»
The committee also found that the ICA suppressed intelligence that showed that Russia was actually planning for a Clinton victory because «they knew where (she) stood» and believed Russia «could work with her.»
The declassification of the report comes just days after Gabbard declassified and released documents that included «overwhelming evidence» that demonstrated how, after Trump won the 2016 election against Clinton, then-President Obama and his national security team laid the groundwork for what would be the yearslong Trump–Russia collusion probe.
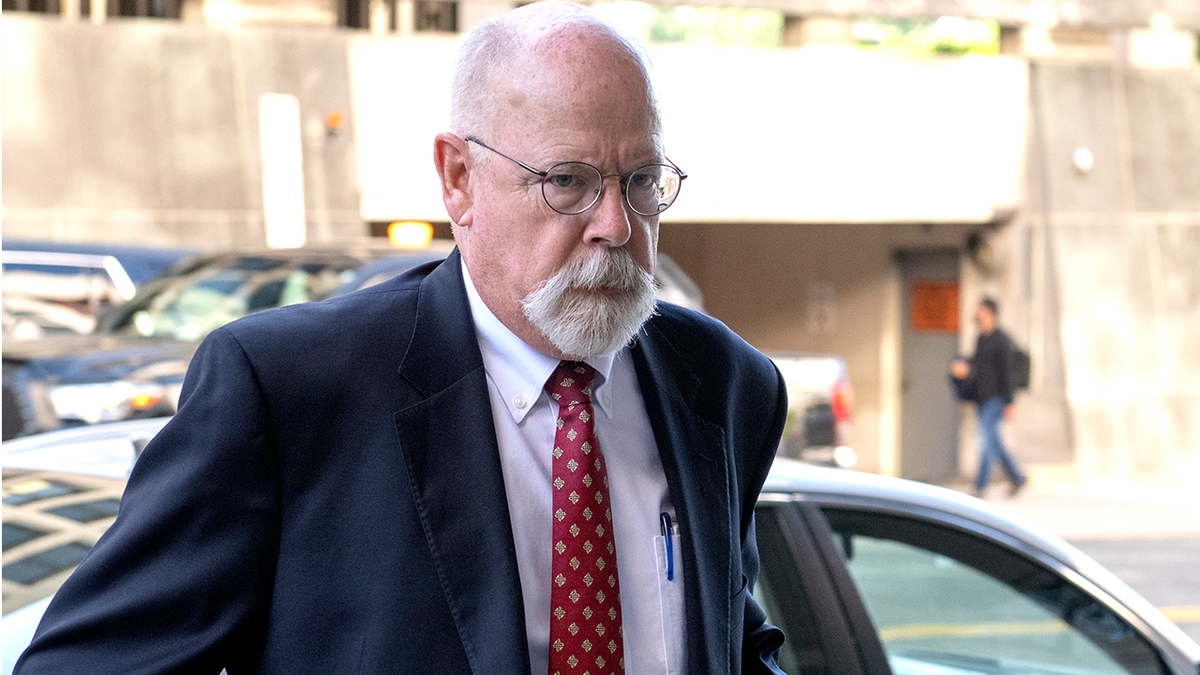
Special Counsel John Durham (Ron Sachs/Consolidated News Pictures/Getty Images)
Meanwhile, Fox News Digital, in 2020, exclusively obtained the declassified transcripts from Obama-era national security officials’ closed-door testimonies before the House Intelligence Committee, in which those officials testified that they had no «empirical evidence» of a conspiracy between the Trump campaign and Russia in the 2016 election, but continued to publicly push the «narrative» of collusion.
DURHAM TESTIFIES THAT THE FBI IGNORED HILLARY CLINTON PLAN TO LINK TRUMP TO RUSSIA
The House Intelligence Committee, in 2017, conducted depositions of top Obama intelligence officials, including Director of National Intelligence James Clapper, National Security Advisor Susan Rice and Attorney General Loretta Lynch, among others.
The transcripts, from 2017 and 2018, revealed top Obama officials were questioned by House Intelligence Committee lawmakers and investigators about whether they had or had seen evidence of such collusion, coordination or conspiracy – the issue that drove the FBI’s initial case and later the special counsel probe.
CLICK HERE TO GET THE FOX NEWS APP
«I never saw any direct empirical evidence that the Trump campaign or someone in it was plotting/conspiring with the Russians to meddle with the election,» Clapper testified in 2017. «That’s not to say that there weren’t concerns about the evidence we were seeing, anecdotal evidence…. But I do not recall any instance where I had direct evidence.»
INTERNACIONAL
Zelenskyy forced to rethink anti-corruption law after public backlash

NEWYou can now listen to Fox News articles!
Ukrainian President Volodymyr Zelenskyy is set to introduce new legislation that will restore the independence of anti-corruption agencies in Ukraine after fierce public opposition and international condemnation over signing a law that targeted Ukraine’s independent anti-corruption institutions.
In a sudden turn of events, Zelenskyy posted a video on X in which he said, «Of course, everyone has heard what people are saying these days – on social media, to each other, on the streets. It’s not falling on deaf ears. We analyzed all concerns, all aspects of what needs to be changed and what needs to be stepped up.
«I will propose a bill to the Verkhovna Rada of Ukraine that will be the response. It will ensure the strength of the rule of law system, and there will be no Russian influence or interference in the activities of law enforcement. And very importantly – all the norms for the independence of anti-corruption institutions will be in place,» he said according to a translated version on the screen.
UKRAINE SEES SWEEPING PROTESTS OVER BILL WEAKENING ANTI-CORRUPTION AGENCIES
Mass protests erupted in Kyiv and across Ukraine in opposition to the law, the largest anti-government demonstrations since Russia’s full-scale invasion began in February 2022. European Commission President Ursula von der Leyen called Zelenskyy to express her strong concerns and convey Brussels’ disapproval of the bill.
One source close to the situation, who asked to remain anonymous, told Fox News Digital that the incident should give President Zelenskyy pause as to whether he is getting the best counsel from his closest people.
The individual with ties to the Ukraine government said this propaganda bonanza for Russia is a self-inflicted wound and also shows the president and his team have misread public sentiment.
Many Ukrainians and Western allies fear the current turmoil could jeopardize their path to join the European Union and fracture society’s unity while the country faces continued Russian onslaughts.
Although he signed the original bill, Zelenskyy said with the announcement of the new bill that it will ensure the independence of anti-corruption bodies and also eliminate Russian influence over their activities. In defending the previous legislation, he claimed that Ukraine’s anti-corruption infrastructure was infiltrated by Russia.
Ukrainians protest in the first wartime rally against a newly passed law, which curbs independence of anti-corruption institutions, amid Russia’s attack on Ukraine, in central Lviv, Ukraine July 22, 2025. (Roman Baluk/Reuters)
The previous bill that passed on Tuesday allowed Ukraine’s Prosecutor General, appointed by the president, wide authority over cases before the National Anti-Corruption Bureau of Ukraine (NABU), an anti-corruption agency that was championed by the United States and Europe. It gave the prosecutor general the sweeping power to transfer cases from NABU and usurp other powers from the Specialized Anti-Corruption Prosecutor’s Office (SAPO), the agency responsible for prosecuting NABU’s cases.
UKRAINE’S ZELENSKYY NAMES NEW PRIME MINISTER FOR FIRST TIME SINCE RUSSIA’S WAR BEGAN
«That is tantamount to being able to squash any legal accountability for corruption,» Josh Rudolph, anti-corruption expert and senior fellow at the German Marshall Fund, told Fox News Digital.
Rudolph noted that the heads of NABU and SAPO are highly reputable professionals and were selected with the concurrence of Ukraine’s international partners, a key component of joining the EU.
«Zelenskyy could have come out as a hero or a villain if he signed the bill. It was a moment of truth,» Orysia Lutsevych, Head of Ukraine Forum, Chatham House, told Fox News Digital. Even though Zelenskyy listened to public opinion and ultimately backed down, his overall popularity continues to take a hit.

Ukrainian President Volodymyr Zelensky and Italian Prime Minister Giorgia Meloni (not in picture) hold a joint press conference during the Ukraine Recovery Conference 2025 (URC2025) at Roma Convention Center La Nuvola, on July 10, 2025 in Rome, Italy (Antonio Masiello/Getty Image)
Ukraine has been plagued by government corruption since declaring independence from the Soviet Union in 1991. Many Ukraine watchers are worried that efforts to rollback anti-corruption initiatives will be fodder for Russian propaganda and fracture Ukraine’s unity at a critical time in the war.
«Russia can and will use Ukraine’s move to restructure anti-corruption agencies to argue lack of unity, support for the government, and internal disagreements. It will again apply its propaganda arguments about legitimacy of Zelenskyy and the need for elections,» Tymofiy Mylovanov, President of Kyiv School of Economics, told Fox News Digital.

In this handout photo taken from video released by Russian Presidential Press Service, Russian President Vladimir Putin addresses the nation in Moscow, Russia, Saturday, June 24, 2023. (Russian Presidential Press Service via AP)
CLICK HERE TO GET THE FOX NEWS APP
Russian President Vladimir Putin claims Zelenskyy is illegitimate and has called for new elections in Ukraine. Elections were scheduled for March 2024 but postponed while the country remains at war and under martial law.
The disunity within Ukraine comes at a time when Russian forces are escalating large-scale missile and drone strikes in Kyiv and across the country. Russian forces continue to make advances while Kyiv urgently pleads with Europe and the United States to send air defense systems and other key weapons to limit Moscow’s battlefield gains.
INTERNACIONAL
Polémica en Estados Unidos: el gobierno de Trump envió cartas con amenazas a niños inmigrantes

En una medida que desató una fuerte polémica, el gobierno de Donald Trump comenzó amenazar a niños inmigrantes para que abandonen el país. Decenas de ellos recibieron cartas con amenazas de deportación.
“Es hora de que salgas de Estados Unidos”, señala la primera línea de una de las cartas que recibieron a su nombre los menores de edad. Y agrega: “No intentes permanecer ilegalmente en Estados Unidos; el Gobierno federal te encontrará”.
Leé también: Lejos de su objetivo, Trump deportó a 239.000 migrantes en seis meses y tiene en la mira a otros 13 millones
Los destinatarios de las advertencias entraron al país legalmente. En las misivas, se los amenaza con deportaciones, multas y procesos penales.
En abril pasado, los tribunales de inmigración ordenaron la deportación de más de 8300 niños de 11 años o menos. Y en los casi ocho meses que lleva la gestión de Trump, los jueces ordenaron la deportación de más de 53.000 niños inmigrantes, según Transactional Records Access Clearinghouse, una organización de la Universidad de Syracuse.
La mayoría de estos niños están en edad de escuela primaria. Aproximadamente 15 mil tenían menos de cuatro años, y otros 20 mil, entre cuatro y 11. Unos 17.000 adolescentes también fueron deportados.
Qué dicen las cartas enviadas a menores inmigrantes
Las cartas desataron una ola de nerviosismo y temor en numerosas familias migrantes. “Actualmente te encuentras aquí porque el Departamento de Seguridad Nacional (DHS) te otorgó un permiso de entrada condicional a Estados Unidos por un período limitado. El DHS está ejerciendo su discreción para cancelar tu permiso de entrada condicional, o ya lo ha hecho”, afirma una de las cartas citadas por EFE. Agentes del Servicio de Inmigración y Control de Aduanas escoltan a un inmigrante detenido hacia un elevador después de salir de un tribunal de inmigración, el martes 17 de junio de 2025, en Nueva York. (AP Foto/Olga Fedorova, Archivo)
En otro de los párrafos, se lee: “Si no sales de Estados Unidos de inmediato, estarás sujeto a posibles medidas policiales que resultarán en tu deportación”.
“Esto es algo nunca visto”
Las cartas causaron enorme malestar y temor en las comunidades de inmigrantes. “Esto es una barbaridad, algo nunca visto o imaginado por todos lo que nos dedicamos a la defensa de los (migrantes) indocumentados”, dijo la pastora Julie Contreras, del santuario United Giving Hope, que tiene sede en la ciudad de Waukegan, Illinois, 74 kilómetros al norte de Chicago.
Y agregó: “Imaginen qué pasa por la cabeza de un niño al recibir una carta de este tipo de parte del Gobierno del país más poderoso del mundo, que les niega el permiso humanitario. Esto es muy grave y fuerte”.
Leé también: La historia del chileno que perdió su documento en EEUU, lo dieron por muerto y fue deportado a Guatemala
Decenas de niños del área de Waukegan, que cruzaron la frontera sin sus padres, en su mayoría desde México, recibieron cartas de deportación. Todos ellos ingresaron legalmente al país en 2014 bajo un programa humanitario como “menores no acompañados” para, posteriormente, reunirse con sus padres indocumentados u otros familiares que ya vivían en Estados Unidos.
A pesar de la reunificación, los menores no pueden ser representados legalmente por sus padres en un tribunal de inmigración por la forma en que ingresaron al país, y dependen de abogados defensores que vieron su trabajo reducido por falta de recursos.
“Estos niños no son criminales”
Según Contreras, las cartas pueden ser un cambio “preocupante y alarmante” porque ahora se buscaría despojar a los niños de las protecciones de asilo, incluso a aquellos con solicitudes pendientes, y acelerar la deportación de menores sin el debido proceso.
“Estos niños no son los criminales que Trump afirmó que el ICE perseguiría. Son víctimas de violaciones de derechos humanos y están siendo aterrorizados. Incluso si el ICE no los busca de inmediato, la sola amenaza les causa un grave trauma psicológico”, dijo.
Tres de esos niños, acompañados de madres o tías, buscaron la protección de “santuario” en la iglesia de Contreras. Un cuarto fue dejado solo al cuidado de la iglesia porque sus padres tienen miedo. “Estados Unidos está perdiendo su humanidad, las iglesias y otros santuarios ya no ofrecen garantías”, afirmó la pastora.

El presidente estadounidense Donald Trump busca acelerar las deportaciones (Foto: AP Foto/Alex Brandon)
El silencioso desmantelamiento legal
La ley de inmigración establece que los menores no acompañados que llegan a la frontera sin un padre o tutor legal deben recibir protección especial: son puestos bajo el cuidado de la Oficina de Reubicación de Refugiados (ORR, por sus siglas en inglés) y se les otorga un permiso humanitario mientras se procesan sus casos.
Pero en los últimos meses, defensores de los migrantes y abogados afirman que el sistema se está desmantelando silenciosamente.
Leé también: En medio de la tensión por el caso Epstein, Trump acusó a Obama de traición e intento de golpe de Estado
Cada vez más menores no acompañados ven revocado su permiso humanitario y son encarcelados en procesos migratorios donde no tienen ninguna capacidad para defenderse, dijo a medios locales Davina Casas, pastora y líder de la Organización Monarquía, de Chicago.
Casas explicó que en marzo la Administración Trump recortó los fondos para abogados de menores no acompañados, y solo tras una demanda de 11 grupos defensores se restablecieron temporalmente por orden judicial, aunque el caso sigue abierto.
Los grupos sostienen que, según una ley contra la trata de 2008, el Gobierno debe ofrecer asistencia legal y garantizar la repatriación segura de los niños. Pero Casas duda que, incluso con fondos restablecidos, la demanda pueda ser cubierta.
(Con información de EFE)
inmigracion, Estados Unidos, Donald Trump

 POLITICA3 días ago
POLITICA3 días agoLa CGT evalúa adelantar a octubre el recambio de sus autoridades y define una movilización contra Milei

 POLITICA2 días ago
POLITICA2 días ago🗳️ El chamuyo de las elecciones en la Provincia: se postulan, pero no a asumen

 POLITICA2 días ago
POLITICA2 días agoFuerte malestar en la CGT por la ausencia de gremialistas en las listas bonaerenses del peronismo























