INTERNACIONAL
China’s missile surge puts every US base in the Pacific at risk — and the window to respond is closing

NEWYou can now listen to Fox News articles!
China has spent decades building a land-based missile force designed to keep the United States out of a fight over Taiwan — and U.S. officials say it now threatens every major airfield, port and military installation across the Western Pacific.
As Washington races to build its own long-range fires, analysts warn that the land domain has become the most overlooked — and potentially decisive — part of the U.S.–China matchup. Interviews with military experts show a contest defined not by tanks or troop movements, but by missile ranges, base access and whether U.S. forces can survive the opening salvos of a war that may begin long before any aircraft take off.
«The People’s Liberation Army Rocket Force … has built an increasing number of short-, medium-, and long-range missiles,» Seth Jones of the Center for Strategic and International Studies told Fox News Digital. «They have the capability to shoot those across the first and increasingly the second island chains.»
For years, Chinese officials assumed they could not match the United States in air superiority. The Rocket Force became the workaround: massed, land-based firepower meant to shut down U.S. bases and keep American aircraft and ships outside the fight.
HIGH STAKES ON THE HIGH SEAS AS US, CHINA TEST LIMITS OF MILITARY POWER
«They didn’t think that they could gain air superiority in a straight-up air-to-air fight,» said Eric Heginbotham, a research scientist at the Massachusetts Institute of Technology. «So you need another way to get missiles out — and that another way is by building a lot of ground launchers.»
«The People’s Liberation Army Rocket Force… has built an increasing number of short-, medium-, and long-range missiles,» Seth Jones of the Center for Strategic and International Studies told Fox News Digital. (CNS Photo via Reuters)
The result is the world’s largest inventory of theater-range missiles, backed by hardened underground facilities, mobile launchers and rapid shoot-and-scoot tactics designed to overwhelm U.S. defenses.
Despite China’s numerical edge, American forces still hold advantages Beijing has not yet matched — particularly in targeting and survivability.
U.S. missiles, from Tomahawks to SM-6s to future hypersonic weapons, are tied into a global surveillance network the People’s Liberation Army cannot yet replicate. American targeting relies on satellites, undersea sensors, stealth drones and joint command tools matured over decades of combat experience.
«The Chinese have not fought a war since the 1970s,» Jones said. «We see lots of challenges with their ability to conduct joint operations across different services.»
The U.S., by contrast, has built multi-domain task forces in the Pacific to integrate cyber, space, electronic warfare and precision fires — a level of coordination analysts say China has yet to demonstrate.
Jones said China’s defense industry also faces major hurdles.
«Most of (China’s defense firms) are state-owned enterprises,» he said. «We see massive inefficiency, the quality of the systems … we see a lot of maintenance challenges.»
Still, the United States faces a near-term problem of its own: missile stockpiles.
«We still right now … would run out (of long-range munitions) after roughly a week or so of conflict over, say, Taiwan,» Jones said.
SKIES AT STAKE: INSIDE THE US-CHINA RACE FOR AIR DOMINANCE
Washington is trying to close that gap by rapidly expanding production of ground-launched weapons. New Army systems — Typhon launchers, high mobility artillery rocket system, batteries, precision strike missiles and long-range hypersonic weapons with a range exceeding 2,500 kilometers — are designed to hold Chinese forces at risk from much farther away.
Heginbotham said the shift is finally happening at scale.
«We’re buying anti-ship missiles like there’s no tomorrow,» he said.
If current plans hold, U.S. forces will field roughly 15,000 long-range anti-ship missiles by 2035, up from about 2,500 today.
China’s missile-heavy strategy is built to overwhelm U.S. bases early in a conflict. The United States, meanwhile, relies on layered air defenses: Patriot batteries to protect airfields and logistics hubs, terminal high altitude area defense (THAAD) interceptors to engage ballistic missiles at high altitude, and Aegis-equipped destroyers that can intercept missiles far from shore.
Heginbotham warned the U.S. will need to widen that defensive mix.
«We really need a lot more and greater variety of missile defenses and preferably cheaper missile defenses,» he said.
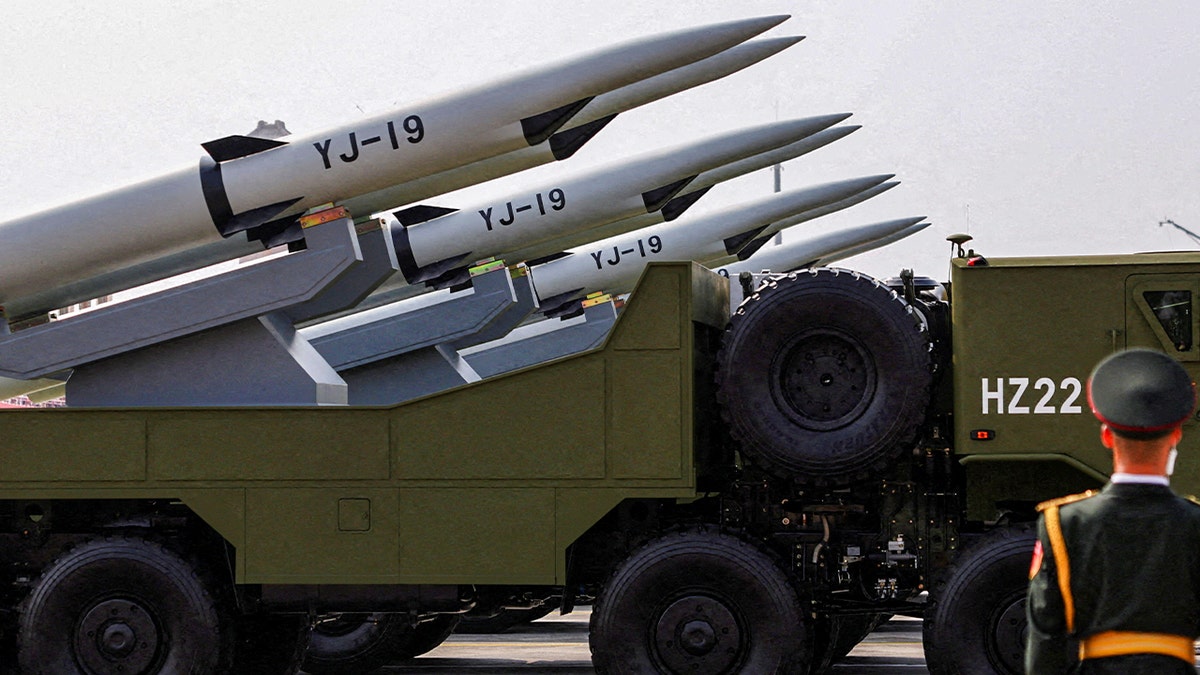

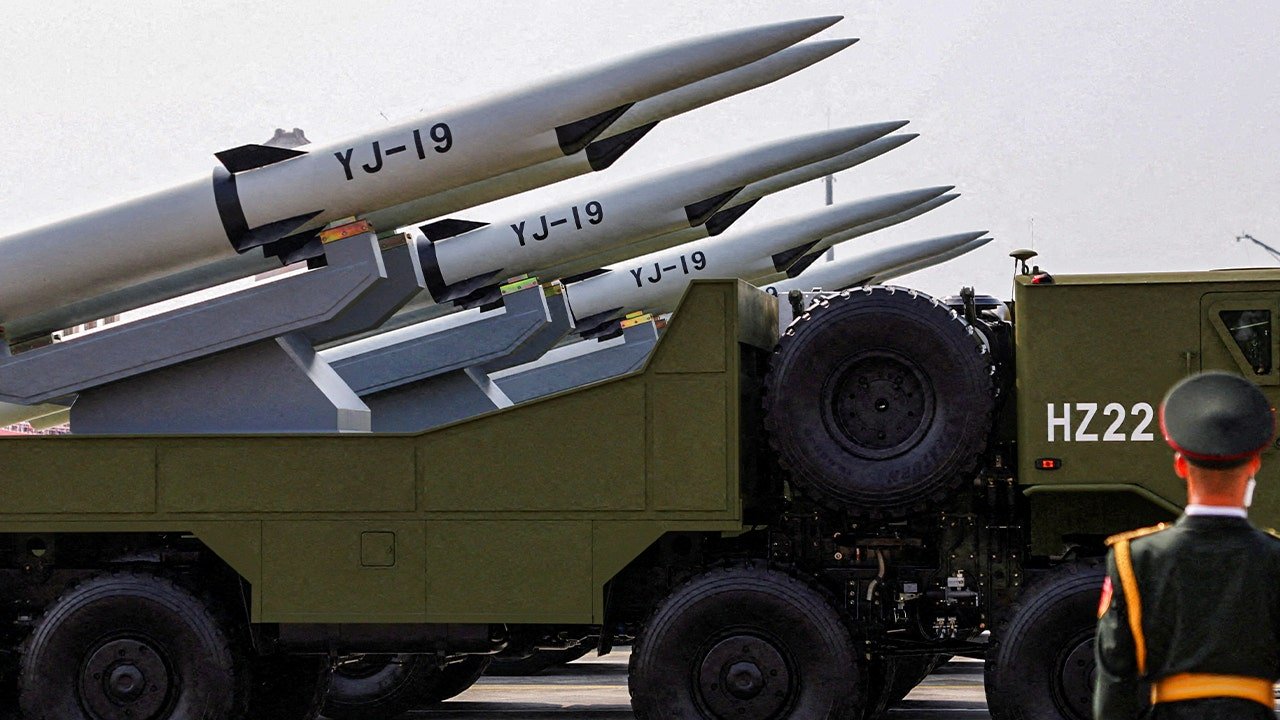
A member of the People’s Liberation Army stands as the maritime operations group displays YJ-19 hypersonic anti-ship missiles during a military parade to mark the 80th anniversary of the end of World War Two, in Beijing, China, Sept. 3, 2025. (Tingshu Wang/Reuters)
One of Washington’s biggest advantages is its ability to conduct long-range strikes from beneath the ocean. U.S. submarines can fire cruise missiles from virtually anywhere in the Western Pacific, without relying on allied basing and without exposing launchers to Chinese fire — a degree of stealth China does not yet possess.
Command integration is another area where Beijing continues to struggle. American units routinely train in multi-domain operations that knit together air, sea, cyber, space and ground-based fires.
Jones and Heginbotham both noted that the People’s Liberation Army has far less experience coordinating forces across services and continues to grapple with doctrinal and organizational problems, including the dual commander–political commissar structure inside its missile brigades.
Alliances may be the most consequential difference. Japan, the Philippines, Australia and South Korea provide depth, intelligence sharing, logistics hubs and potential launch points for U.S. forces.
China has no comparable network of partners, leaving it to operate from a much narrower geographic footprint. In a missile war, accuracy, integration and survivability often matter more than sheer volume — and in those areas the United States still holds meaningful advantages.
At the heart of this competition is geography. Missiles matter less than the places they can be launched from, and China’s ability to project power beyond its coastline remains sharply constrained.
«They’ve got big power-projection problems right now,» Jones said. «They don’t have a lot of basing as you get outside of the first island chain.»
The United States faces its own version of that challenge. Long-range Army and Marine Corps fires require host-nation permission, turning diplomacy into a form of firepower.
«It’s absolutely central,» Heginbotham said. «You do need regional basing.»
Recent U.S. agreements with the Philippines, along with expanded cooperation with Japan and Australia, reflect a push to position American launchers close enough to matter without permanently stationing large ground forces there.
A U.S.–China land conflict would not involve armored columns maneuvering for territory. The decisive question is whether missile units on both sides can fire, relocate and fire again before being targeted.
China has invested heavily in survivability, dispersing its brigades across underground bunkers, tunnels and hardened sites. Many can fire and relocate within minutes. Mobile launchers, decoys and deeply buried storage complexes make them difficult to neutralize.

U.S. forces will field roughly 15,000 long-range anti-ship missiles by 2035, up from about 2,500 today. (Daniel Ceng/Anadolu via Getty Images)
U.S. launchers in the Pacific would face intense Chinese surveillance and long-range missile attacks. After two decades focused on counterterrorism, the Pentagon is now reinvesting in deception, mobility and hardened infrastructure — capabilities critical to surviving the opening stages of a missile war.
Any U.S. intervention in a Taiwan conflict would also force Washington to confront a politically charged question: whether to strike missile bases on the Chinese mainland. Doing so risks escalation; avoiding it carries operational costs.
«Yes … you can defend Taiwan without striking bases inside China,» Heginbotham said. «But you are giving away a significant advantage.»
Holding back may help prevent the conflict from widening, but it also allows China to keep firing.
«It’s a reality of conflict in the nuclear age that almost any conflict is gonna be limited in some ways,» Heginbotham said. «Then the question becomes where those boundaries are drawn, can you prevent it from spreading? What trade-offs you’re willing to accept?»
A U.S.–China clash on land would not be fought by massed armies. It would be a missile war shaped by geography, alliances and survivability — a contest where political access and command integration matter as much as raw firepower.
CLICK HERE TO DOWNLOAD THE FOX NEWS APP
For the United States, the challenge is clear: build enough long-range missiles, secure the basing needed to use them and keep launchers alive under fire. For China, the question is whether its vast missile arsenal and continental depth can offset weaknesses in coordination, command structure and real-world combat experience.
The side that can shoot, relocate and sustain fire the longest will control the land domain — and may shape the outcome of a war in the Pacific.
This is the third installment of a series comparing U.S. and Chinese military capabilities. Feel free to check out earlier stories comparing sea and air capabilities.
china,conflicts defense,military tech
INTERNACIONAL
El régimen iraní identificó a casi 3.000 muertos por la represión mientras la ONU estima que la cifra llegaría a cerca de 20.000
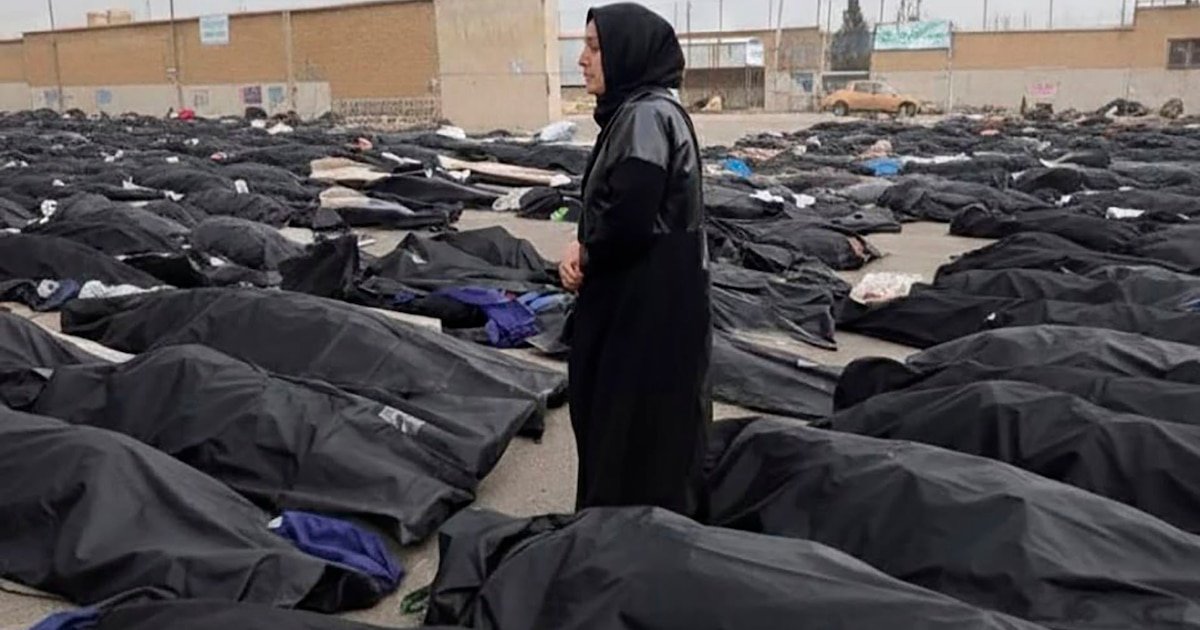

El régimen iraní publicó este domingo una lista con los nombres de 2.986 personas fallecidas durante la represión de las protestas que comenzaron en diciembre, un balance que Teherán cifra en 3.117 muertos totales. Sin embargo, la Organización de las Naciones Unidas y organizaciones de derechos humanos advierten que la magnitud real de la masacre perpetrada por la República Islámica podría ser entre seis y diez veces superior, con estimaciones que alcanzan las 20.000 víctimas mortales.
“Me gustaría informar con tristeza a la noble nación de Irán que el número total de víctimas de los recientes acontecimientos es de 3.117”, afirmó el presidente Masud Pezeshkian en un comunicado oficial. El mandatario iraní explicó que la diferencia de 131 personas entre el total declarado y la lista publicada “se debe a la identidad desconocida de varias personas y a las discrepancias en el registro del documento nacional de identidad”, que serán incluidas en una lista complementaria una vez corregidas.
Pezeshkian anunció además que en las próximas 48 horas se habilitará un sistema para que “cualquier nueva información y reclamación pueda ser examinada y verificada sin complicaciones administrativas”.
El comunicado presidencial mantiene la línea argumental del régimen, que atribuye el elevado número de víctimas a “terroristas” respaldados por Estados Unidos e Israel. “Los enemigos históricos y los detractores comercian con las vidas de las personas como si fueran un número”, afirmó Pezeshkian, sin hacer referencias específicas.
Las cifras oficiales, sin embargo, contrastan drásticamente con los datos recabados por organismos internacionales. La relatora especial de la ONU para Irán, Mai Sato, declaró a medios estadounidenses que informes de médicos dentro del país indican que las víctimas mortales podrían alcanzar las 20.000 personas.
“La magnitud de los fallecidos y heridos por la represión de las protestas a lo largo de este mes ha sido enorme, de miles de personas”, confirmó Ravina Shamdasani, portavoz de la Oficina de Naciones Unidas para los Derechos Humanos, aunque reconoció que es “difícil verificar las informaciones que llegan desde el país dadas las restricciones continuas sobre el terreno”.
Amnistía Internacional y Human Rights Watch han documentado el uso de fuerza letal indiscriminada, con fuerzas de seguridad disparando rifles y escopetas cargadas con perdigones metálicos contra manifestantes desarmados. Las morgues desbordadas, el uso de contenedores refrigerados para almacenar cadáveres y los entierros apresurados sin identificación previa apuntan, según estas organizaciones, a un intento deliberado de ocultar la verdadera escala de la masacre.
El apagón casi total de internet impuesto por el régimen desde el 8 de enero ha sido clave para dificultar la verificación independiente. NetBlocks, organización de monitoreo de ciberseguridad, confirmó que se trata del bloqueo digital más prolongado en la historia de Irán, con el objetivo explícito de impedir que los ciudadanos difundan imágenes de la represión y de aislar al país del escrutinio internacional. Esta desconexión ha permitido que las fuerzas de seguridad actúen con mayor impunidad, según denunciaron organizaciones de derechos humanos.
Las protestas estallaron el 28 de diciembre de 2025 en el Gran Bazar de Teherán, inicialmente motivadas por el colapso económico que atraviesa Irán. La tasa de inflación alcanzó el 42,2% en diciembre, con un aumento del 72% en el precio de los alimentos. El rial iraní se depreció drásticamente, con el dólar estadounidense alcanzando los 145.000 tomanes.
Lo que comenzó como huelgas de comerciantes se transformó rápidamente en manifestaciones masivas en las 31 provincias del país, con cánticos contra el líder supremo Ali Khamenei y exigencias de cambio del sistema político. Se trata de las protestas más grandes desde los disturbios de 2022 tras la muerte de Mahsa Amini bajo custodia policial.
La represión alcanzó su punto más crítico los días 8 y 9 de enero, cuando el líder supremo Khamenei ordenó al Consejo Supremo de Seguridad Nacional reprimir las protestas “por cualquier medio necesario”, según informaron funcionarios iraníes a medios internacionales.
Las fuerzas de seguridad recibieron la orden de disparar para matar sin mostrar piedad. The New York Times verificó videos que muestran a agentes abriendo fuego contra manifestantes en al menos 19 ciudades y seis barrios de Teherán. En la ciudad de Fardis, testigos alegan que más de 50 manifestantes fueron abatidos tras el despliegue de una ametralladora montada en un vehículo.
El Consejo de Derechos Humanos de la ONU aprobó la semana pasada, en una sesión de emergencia, una resolución con 25 votos a favor que denuncia que la represión violenta “ha resultado en la muerte de miles de personas, incluyendo niños, y un gran número de heridos”.
El texto, respaldado por Francia, Italia, España y Reino Unido, instó a las autoridades iraníes a poner fin a las ejecuciones extrajudiciales, las desapariciones forzadas, la tortura y otros abusos contra manifestantes pacíficos. La resolución prorrogó dos años más el mandato de la Misión Internacional Independiente de Investigación sobre Irán y por un año el de la relatora especial.
INTERNACIONAL
Resurfaced photo links Mamdani to Epstein-connected publicist at New York City event

NEWYou can now listen to Fox News articles!
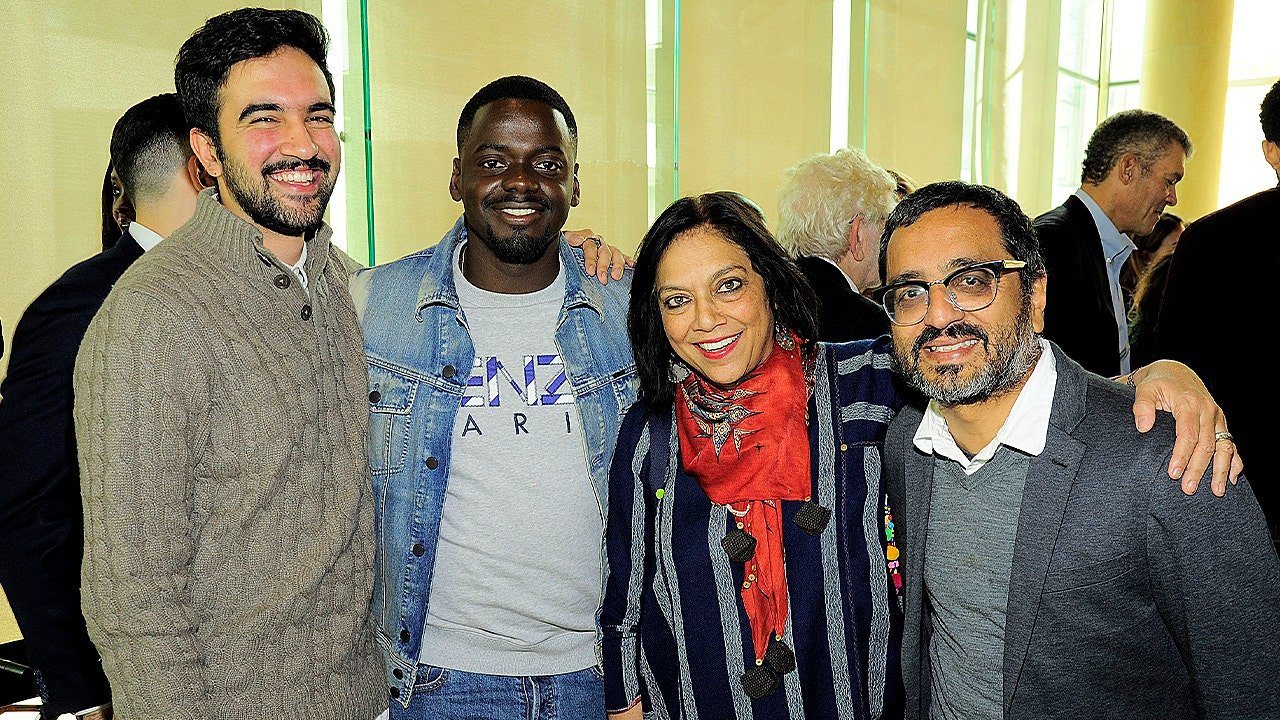
A photo showing Zohran Mamdani at a high-profile luncheon tied to longtime Jeffrey Epstein associate Peggy Siegal has emerged following the release of newly unsealed Justice Department records that also reference his mother, Mira Nair.
The photo, taken Nov. 15, 2017, shows the now-New York City mayor smiling at the Universal Pictures «Get Out» Peggy Siegal luncheon at Lincoln Ristorante in Manhattan.
The event was hosted by Siegal, a once-powerful Hollywood publicist who later faced industry backlash over her deep social ties to Epstein.
Siegal was never charged with a crime.
EPSTEIN FILE RELEASE FEATURES PHOTOS OF MICK JAGGER, MICHAEL JACKSON, DIANA ROSS AND MORE STARS
(L-R) Zohran Mamdani, Daniel Kaluuya, Mira Nair and Shimit Amin attend Universal Pictures’ «Get Out» Peggy Siegal Luncheon at Lincoln Ristorante on November 15, 2017, in New York City. (Owen Hoffmann/Patrick McMullan via Getty Images)
The image surfaced days after filmmaker Nair was named in a newly released tranche of documents connected to Epstein and his convicted accomplice, Ghislaine Maxwell.
The records, made public Jan. 30, 2026, are part of a broader release of millions of pages detailing Epstein’s social and professional network. The documents do not allege criminal wrongdoing by those mentioned.
In a 2009 email included in the release, Siegal wrote to Epstein about an after-party for the film Amelia, which Nair had directed.
The message states the gathering took place at Maxwell’s Manhattan townhouse and lists attendees including former President Bill Clinton, Amazon founder Jeff Bezos and Nair.
The correspondence documents attendance only and does not allege misconduct by those named.
NEW EPSTEIN DOCUMENTS INCLUDE PHOTOS OF BILL CLINTON TOPLESS IN HOT TUB, SOCIALIZING WITH MICHAEL JACKSON

(L-R) Jason Blum, Allison Williams, Jordan Peele, Daniel Kaluuya, Sean McKittrick and Peggy Siegal attend Universal Pictures’ «Get Out» Peggy Siegal Luncheon at Lincoln Ristorante on November 15, 2017, in New York City. (Owen Hoffmann/Patrick McMullan via Getty Images)
In the 2017 luncheon photo, Mamdani appears alongside actor Daniel Kaluuya, filmmaker Shimit Amin and Nair as they celebrated Jordan Peele’s movie, «Get Out,» which won the Academy Award for best original screenplay.
A second image from the same event shows Peele, producer Jason Blum, Allison Williams and Siegal, highlighting the luncheon’s prominence during Hollywood’s awards season.
Another photo from December 2016 also shows Nair attending a private-residence film event with Siegal for «Queen of Katwe.»
CLINTON TEAM DEMANDS TRUMP DOJ RELEASE ‘ANY REMAINING’ DOCS RELATED TO FORMER PRESIDENT, EPSTEIN

(L-R) Peggy Siegal, Lydia Dean Pilcher, Mira Nair, David Oyelowo and Zoe Oyelowo attend Barbara Broccoli and Walt Disney Studios Host a Screening and Reception for «Queen of Katwe» with Mira Nair and David Oyelowo at Private Residence on December 5, 2016, in New York City. (Aurora Rose/Patrick McMullan via Getty Images)
At the time, Siegal was a dominant figure in entertainment publicity, known for her access to major studios, A-list talent and industry power brokers.
In 2019, following reporting that detailed her association with Epstein, multiple Hollywood studios, including Netflix, FX and Annapurna Pictures, cut ties with her, according to Variety.
Epstein was first arrested in Florida in 2006 on charges of procuring a child for prostitution and soliciting a prostitute.
GIANTS CO-OWNER STEVE TISCH RESPONDS AFTER EMAILS BETWEEN HIM AND JEFFREY EPSTEIN INCLUDED IN LATEST DOJ DROP

The Department of Justice has released millions of Epstein documents after President Trump signed the Epstein Files Transparency Act in November. (Patrick McMullan via Getty Images)
He later pleaded guilty, served 13 months in jail with work release and registered as a sex offender.
He died in a Manhattan jail cell in August 2019 while awaiting trial on federal sex-trafficking charges.
Maxwell is serving a 20-year federal prison sentence following her conviction for sex trafficking.
Nair, an internationally respected director known for films including Salaam Bombay!, Monsoon Wedding, The Namesake and Queen of Katwe, has long been a fixture in elite film circles, especially in Manhattan.
CLICK HERE TO DOWNLOAD THE FOX NEWS APP
She is married to academic Mahmood Mamdani.
Fox News Digital has reached out to Zohran Mamdani’s office and Peggy Siegal for comment.
jeffrey epstein,zohran mamdani,ghislaine maxwell,movies,new york city
INTERNACIONAL
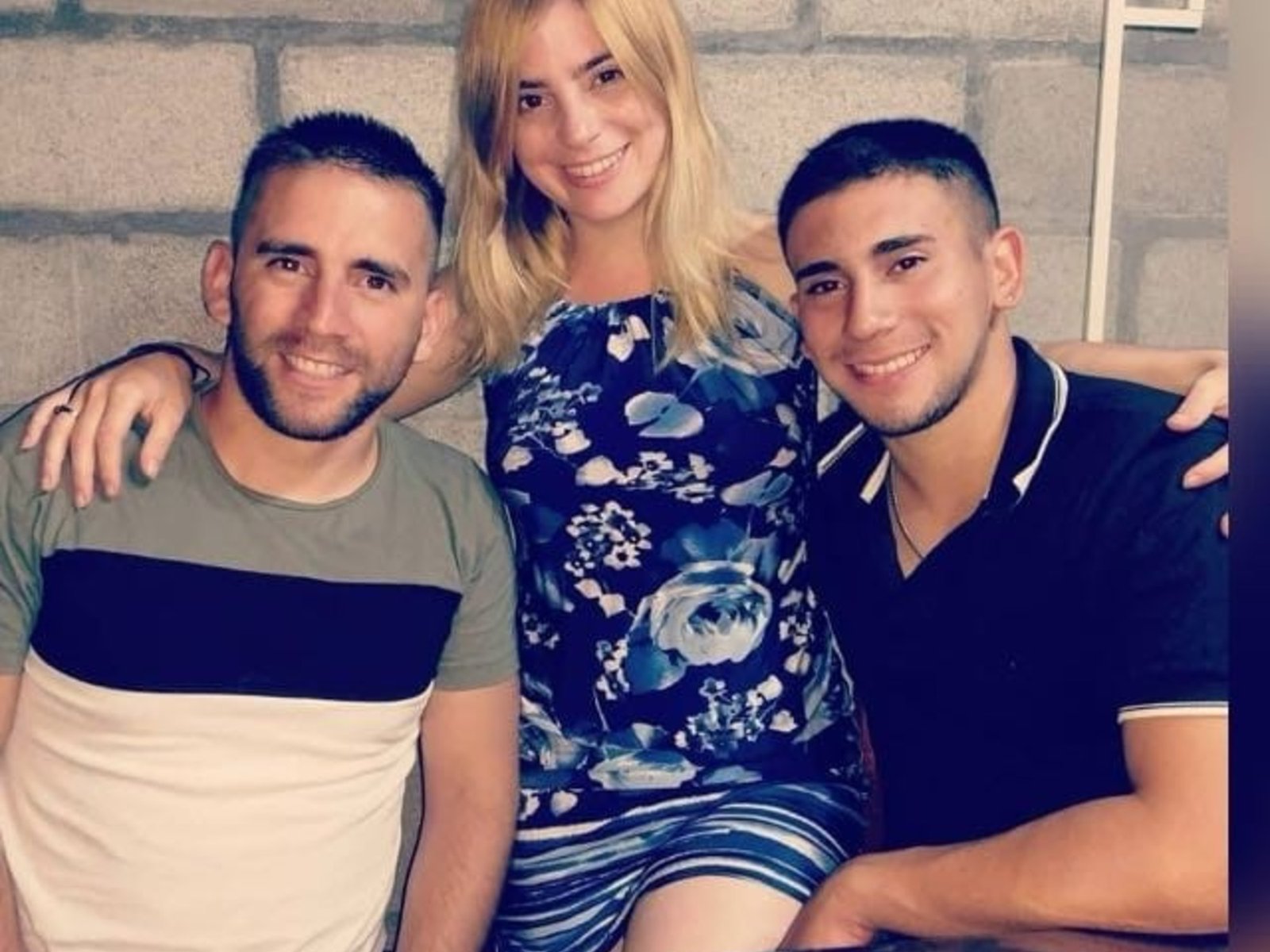
Argentina le pide ayuda a Estados Unidos para liberar a Nahuel Gallo en Venezuela

 CLIMA NOTICIAS2 días ago
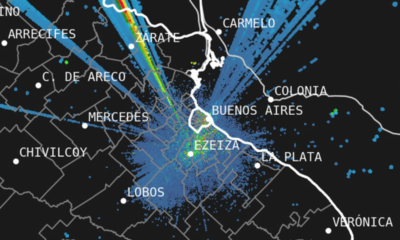
CLIMA NOTICIAS2 días agoA qué hora puede llover hoy en CABA, según el Servicio Meteorológico Nacional

 CHIMENTOS2 días ago
CHIMENTOS2 días agoJulieta Díaz contó por qué no funcionó su noviazgo con Luciano Castro en medio de la separación con Griselda Siciliani

 POLITICA2 días ago
POLITICA2 días agoEl New York Times asegura que la Argentina podría firmar un acuerdo con EE.UU. para recibir deportados