INTERNACIONAL
UK, France, Germany trigger UN sanctions on Iran over ‘significant’ nuclear program defiance

NEWYou can now listen to Fox News articles!
Europe’s powerhouse trio, the U.K., France, and Germany (E3), on Thursday initiated the process to reimpose sweeping sanctions against Iran over its «significant non-compliance» with international nuclear agreements.
At 9 am EST, they submitted a letter to the president of the United Nations Security Council, Panama’s Ambassador Eloy Alfaro de Alba, notifying him of their intent to trigger the snapback sanctions mechanism enshrined under the 2015 nuclear deal known as the Joint Comprehensive Plan of Action (JCPOA).
The action comes after months of warnings from European leaders, and years of calls from the U.S. dating back to the first Trump administration in 2018, flagging that Tehran was in violation of nuclear agreements made under the 2015 Joint Comprehensive Plan of Action (JCPOA) – though Iran’s record of non-compliance did not initiate until 2019 per findings by international nuclear watchdogs.
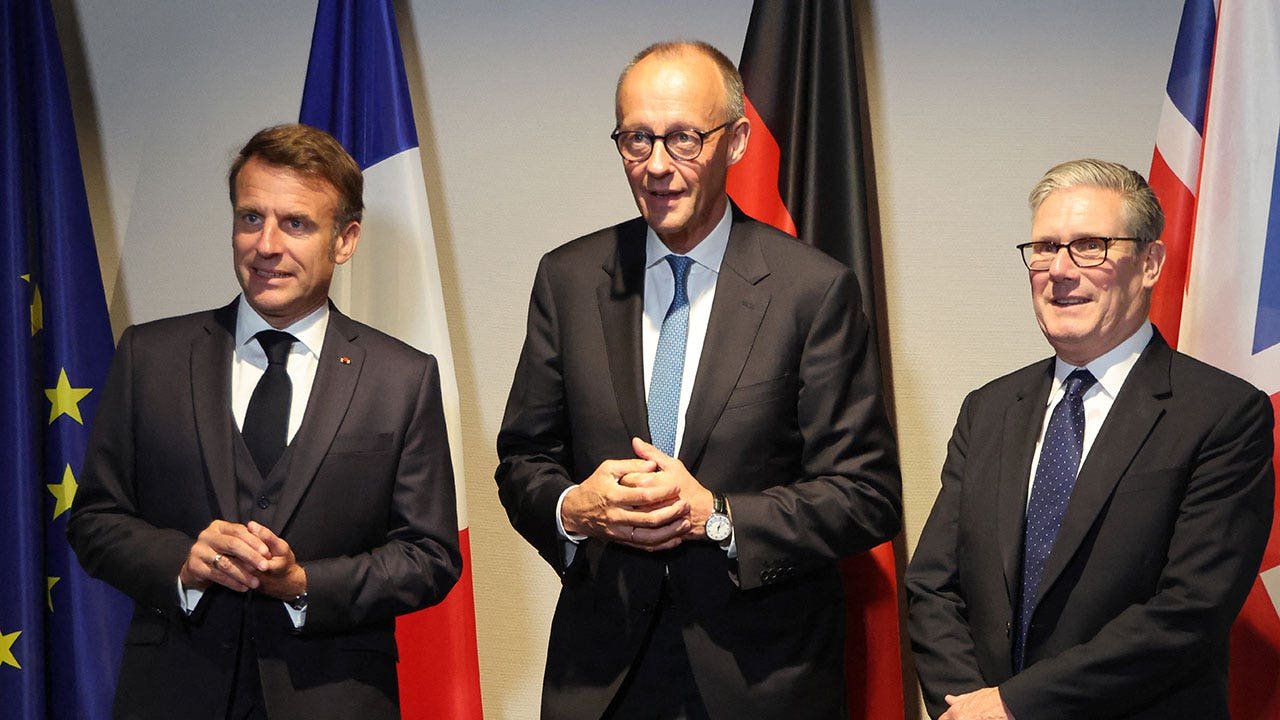
France’s President Emmanuel Macron (L), Germany’s Chancellor Friedrich Merz and Britain’s Prime Minister Keir Starmer pose as they meet on the sidelines of the two-day NATO’s Heads of State and Government summit in The Hague on June 24, 2025. (Ludovic Marin/Pool/AFP via Getty Images)
IRAN SAYS IT HAS ‘PLENTY OF SCIENTISTS’ LEFT TO RESTART URANIUM ENRICHMENT, DESPITE US, ISRAELI STRIKES
According to a U.K. official on Thursday, the decision to enforce snapback sanctions, which is expected to have severe consequences for Iran’s already flagging economy, was not a decision that was made «lightly.»
The official confirmed that there has been «very intense diplomacy» over the last «12-months, 6-months, 6-weeks» that ultimately led to this decision – including three major factors like Tehran’s uranium stockpile levels, its operating of advanced centrifuges and its refusal to adhere to international inspection regulations – all of which are dictated under the JCPOA.
The official confirmed that in May Iran was found to have roughly 20,000 lbs of enriched uranium, including 900 lbs of near-weapons grade highly enriched uranium (HEU) – which is 45 times higher than the JCPOA limit of under 660 lbs of enriched uranium.
«Iran is the only non-nuclear weapons state producing highly enriched uranium,» the official said, adding that those stockpiles remain unaccounted for.
Thursday’s actions mean that by the end of the 30-day period all 15 members of the United Nations Security Council (UNSC), which includes Russia and China, could be legally bound to reimpose sanctions on Iran.
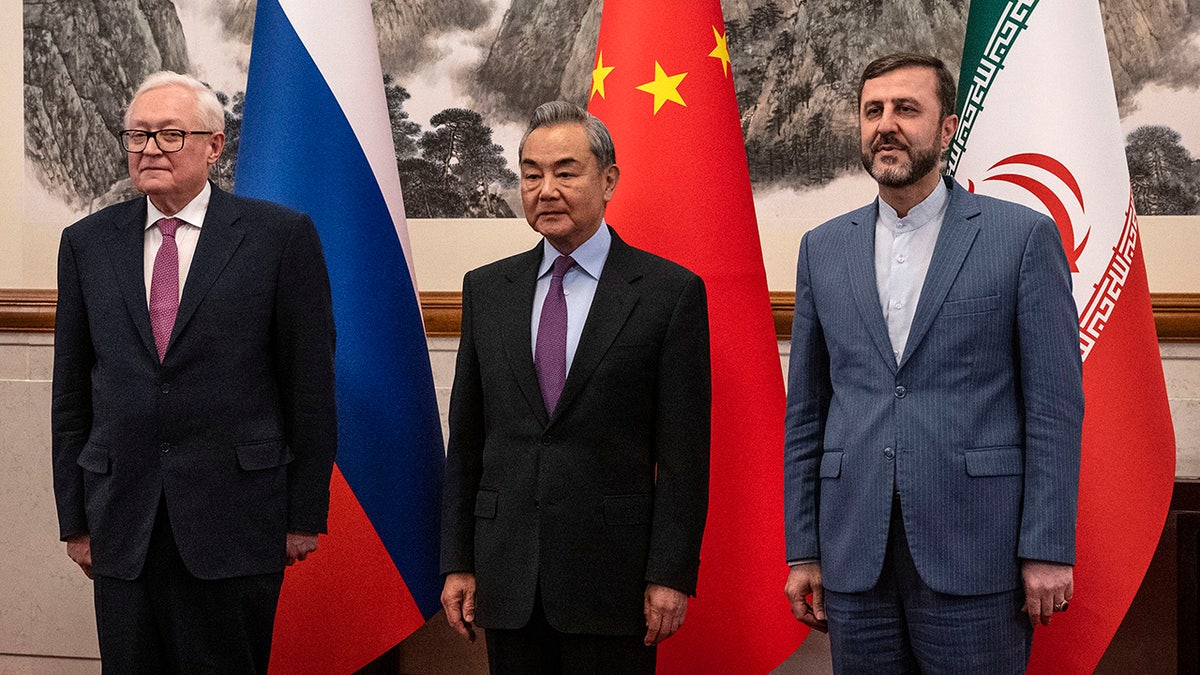

Chinese Foreign Minister Wag Yi, stands with Russian Deputy Foreign Minister Sergey Ryabkov, left, and Iranian Deputy Foreign Minister Kazeem Gharibabadi, right, before a meeting regarding the Iranian nuclear issue at Diaoyutai State Guest House on March 14, 2025 in Beijing, China. (Getty Images)
But in speaking to reporters in Washington, D.C. on Wednesday, the head of the U.N.’s nuclear watchdog, the International Atomic Energy Agency, said there is «still time» for Iran to prevent the sanctions from taking hold.
«Iran will have to comply,» IAEA Director General Raffael Grossi said. «I think there is a possibility. I’m not naively optimistic, but at the same time, there is no reason why we should not [have] a good outcome.»
IRAN DOUBLES DOWN ON REFUSAL TO END NUCLEAR PROGRAM, READY FOR WAR WITH ISRAEL
The E3 and the U.S. have made clear there are specific steps that Tehran needs to do in order to avoid snapback sanctions, including giving the IAEA full access to all Iranian nuclear sites, direct negotiations with Washington, and accounting for roughly 900 lbs of highly enriched uranium (HEU).
But Grossi also noted that it would be «almost impossible» for Iran to get to a point of compliance with the JCPOA due to too many technical advances.
Questions over the location of the HEU, which is estimated to be enough to make 10 nuclear warheads, mounted after the U.S. levied direct strikes at Iran’s nuclear program in June. Reports suggested that in the days leading up to the strikes, Iran may have moved and hidden some of its uranium based on satellite imagery that showed convoys leaving the Fordow and Isfahan nuclear sites.
But on Wednesday, Grossi countered these concerns and said the IAEA had no evidence that the uranium has been moved to a secret location.
Though the stockpile of HEU is still not officially accounted for as the IAEA has not been granted access to Iran’s top nuclear sites – though Grossi said he anticipated that access to come shortly as inspectors on Wednesday visited the Bushehr nuclear power plant after being re-granted access in Iran.
When asked by reporters whether Iran was taking immediate action to begin meeting the E3 demands and avoid sanctions, Grossi said, «point blank…no.»
«Our work hasn’t started. We are not yet where I would like us to be – I will not hide this,» he said. «But at the same time I am a diplomat, I am always working towards peace.»
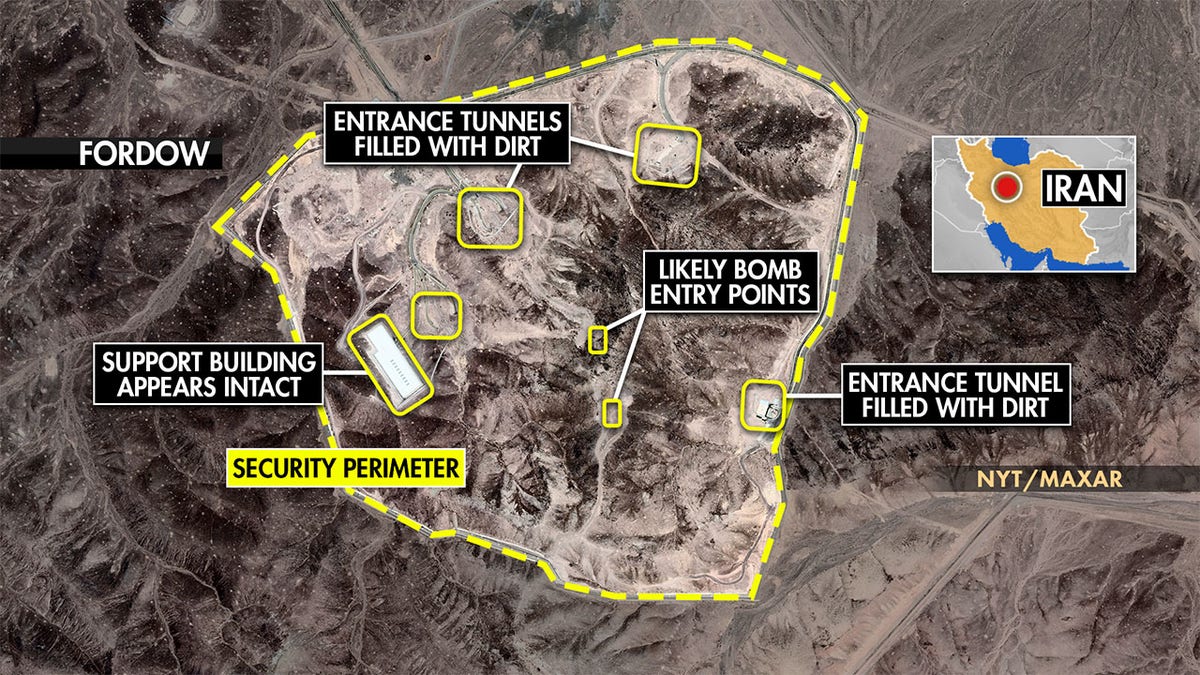
A map shows damage to Iran’s Fordow nuclear site after being struck by the United States in Operation Midnight Hammer on June 22, 2025. (Fox News)
IRAN SEEKS CHINA, RUSSIA HELP TO STALL UN SANCTIONS AHEAD OF NUCLEAR TALKS WITH EUROPEANS
Iran has threatened to retaliate if the sanctions are implemented, though how it will do so remains unclear.
Tehran in recent years has strengthened ties with powerful allies like Russia and China, who have rejected calls for snapback sanctions.
But even though Russia and China sit on the U.N. Security Council with veto powers, they will not be able to unilaterally stop the sanctions from going through.
In an unprecedented move in 2015, the sanctions mechanism was written in a way that reversed standard council procedure, which would traditionally require all five permanent members to approve of any action, meaning that just one veto could block the action.

Members of the UN Security Council attend a meeting on threats to international peace and security at the United Nations Headquarters in New York City on June 13, 2025. (Michael M. Santiago/Getty Images)
CLICK HERE TO GET THE FOX NEWS APP
In the case of snapback sanctions on Iran, every permanent member, which includes the U.S., France, U.K., China and Russia, must veto the push to reimpose sanctions.
This means that, despite opposition from Russia and China, they cannot block the sanctions, as they have increasingly done when it comes to other security council actions in recent years – leading to what some have argued is a paralyzed state in the U.N.’s highest body.
iran,nuclear proliferation,united kingdom,france,germany,united nations,world
INTERNACIONAL
Mamdani’s response to Trump’s Iran strike sparks conservative backlash: ‘Rooting for the ayatollah’

NEWYou can now listen to Fox News articles!
New York City’s socialist Mayor Zohran Mamdani is facing blowback from conservatives on social media over his post condemning the U.S. attack on Iran that led to the killing of Iran’s supreme leader, Ayatollah Ali Khamenei.
On Saturday, as a joint strike on Iran by the United States and Israel was developing, Mamdani blasted the Trump administration’s decision in a post on X that has been viewed roughly 20 million times.
«Today’s military strikes on Iran — carried out by the United States and Israel — mark a catastrophic escalation in an illegal war of aggression,» Mamdani wrote.
«Bombing cities. Killing civilians. Opening a new theater of war. Americans do not want this. They do not want another war in pursuit of regime change.»
New York City Mayor Zohran Mamdani speaks to reporters during a news conference in New York Feb. 17, 2026. (AP Photo/Seth Wenig)
Mamdani said Americans prefer «relief from the affordability crisis» before speaking directly to Iranians in New York City.
«You are part of the fabric of this city — you are our neighbors, small business owners, students, artists, workers, and community leaders,» Mamdani said. «You will be safe here.»
The post was quickly slammed by conservatives on social media making the case that Mamdani’s response appeared sympathetic to Iran’s brutal regime and pointing to his lack of public reaction to the Iranian protesters killed in recent years.
«Comrade Mayor is rooting for the Ayatollah,» GOP Sen. Ted Cruz posted on X. «They can chant together.»
OBAMA OFFICIAL WHO BACKED IRAN DEAL SPARKS ONLINE OUTRAGE WITH REACTION TO TRUMP’S STRIKE: ‘SIT THIS ONE OUT’
«Do u say anything pro American ?» Fox News host Brian Kilmeade posted on X. «do u know any Iranians – ? they hate @fr_Khamenei they celebrate his death, you should be celebrating his death ! hes killed thousands of American’s and just killed 30k Iranians, did u even say a word about that? You are an embarrassment !! Please quit.»

Sen. Ted Cruz, R-Texas, questions Pam Bondi, President-elect Donald Trump’s nominee to be attorney general, during her Senate Judiciary Committee confirmation hearing in Hart building Jan. 15, 2025. (Tom Williams/CQ-Roll Call, Inc via Getty Images)
«I don’t feel safe in New York listening to someone like you, Mamdani, who sympathizes with the regime that killed more than 30,000 unarmed Iranians in less than 24 hours,» Iranian American journalist Masih Alinejad posted on X.
«We Iranians do not allow you to lecture us about war while you had nothing to say when the Islamic Republic shot schoolgirls and blinded more than 10,000 innocent people in the streets. You were busy celebrating the hijab while women of my beloved country Iran were jailed and raped by Islamic Security forces for removing it.
«And NOW you find your voice to defend the regime? No. I will not let you claim the moral high ground. The people of Iran want to be free. Where were you when they needed solidarity?»
CLICK HERE TO DOWNLOAD THE FOX NEWS APP
«How is it that you can’t differentiate between good and evil?» Billionaire hedge fund manager Bill Ackman posted on X. «Why is this so hard for you?»
«It takes a particular kind of audacity, or ignorance, for a city mayor to appoint himself the conscience of American foreign policy while his constituents step over garbage on their way to work,» GOP Rep. Nancy Mace posted on X. «History will not remember his bravery. It will not remember him at all.»
«Iranian New Yorkers are thrilled today and see right through you,» Republican New York City Councilwoman Vickie Paladino posted on X.

Bill Ackman, CEO of Pershing Square Capital Management LP, speaks during the WSJ D.Live global technology conference in Laguna Beach, Calif., Oct. 17, 2017. (Patrick Fallon/Bloomberg/Getty Images)
«When Kuwait, Saudi Arabia, Qatar, Turkey, UAE, Bahrain all support today’s operation eliminating world’s #1 sponsor of terror, but New York City’s Mayor @ZohranMamdani is shilling for Iran,» Republican New York City Councilwoman Inna Vernikov posted on X.
Fox News Digital reached out to Mamdani’s office for comment.
Shortly after Mamdani’s post, it was announced by President Trump and Israeli officials that the military operation resulted in Khamenei’s death.
Israeli leaders confirmed Khamenei’s compound and offices were reduced to rubble early Saturday after a targeted strike in downtown Tehran.
«Khamenei was the contemporary Middle East’s longest-serving autocrat. He did not get to be that way by being a gambler. Khamenei was an ideologue, but one who ruthlessly pursued the preservation and protection of his ideology, often taking two steps forward and one step back,» Behnam Ben Taleblu, senior director of FDD’s Iran program, told Fox News Digital.
war with iran,zohran mamdani,politics
INTERNACIONAL
Iran goes dark amid ‘regime paranoia’, blackout follows Israeli, US strikes on compound

NEWYou can now listen to Fox News articles!
Iran was plunged into an internet blackout Saturday after Israel and the U.S. launched military strikes around the country, according to a global internet monitor.
Within hours of the strikes — which officials said targeted infrastructure and killed dozens of senior regime figures at a compound in Tehran— NetBlocks CEO Alp Toker confirmed connectivity started «flatlining.»
«We’re tracking the ongoing blackout, but our assessment is that this is straight out of Iran’s wartime playbook and consistent both technically and strategically with what we saw during the 2025 Twelve-Day War with Israel,» Toker told Fox News Digital.
«Iran’s internet connectivity is now flatlining around the 1% level, so the original blackout the regime imposed during the morning has been consolidated,» he confirmed.
«The blackout was imposed just after 7:00 UTC, not long after the attack on the Iranian regime compound,» Toker clarified, adding that Iran had been largely offline for approximately 12 hours following the attack.
«At 06:10 UTC, there is the main compound strike; at 07:10 UTC, telecoms disruption starts; at 08:00 UTC, the blackout is largely in effect; and by 08:30 UTC, connectivity flatlines.»
«Wartime national blackouts are exceedingly rare around the world, and it’s something we’ve only really seen at this scale in Iran,» he said.
President Donald Trump monitors U.S. military operations in Iran following an Israeli strike in Tehran on Saturday, Feb. 28, 2026. (@WhiteHouse/X)
In the wake of the attack, dubbed Operation Epic Fury, President Donald Trump said on Truth Social that the «heavy and pinpoint» bombing in Iran «will continue uninterrupted throughout the week or as long as necessary to achieve our objective of PEACE THROUGHOUT THE MIDDLE EAST AND, INDEED, THE WORLD!»
He claimed Iranian security forces and members of the regime’s powerful Islamic Revolutionary Guard Corps were already seeking immunity. He urged them to «peacefully merge with the Iranian Patriots.»
«We are hearing that many of their IRGC, Military, and other Security and Police Forces no longer want to fight and are looking for Immunity from us,» Trump said in the post. «As I said last night, ‘Now they can have Immunity; later they only get Death!’»
Toker argued the timing of the blackout suggested it was imposed deliberately as the regime sought to secure communications amid fears of further targeting.
TRUMP TELLS IRANIANS THE ‘HOUR OF YOUR FREEDOM IS AT HAND’ AS US-ISRAEL LAUNCH STRIKES AGAINST IRAN

TEHRAN, IRAN – FEBRUARY 28: Smoke rises over the city center after an Israeli army launches 2nd wave of airstrikes on Iran on February 28, 2026. (Photo by Fatemeh Bahrami/Anadolu via Getty Images) (Fatemeh Bahrami/Anadolu via Getty Images)
«The Iranian regime will have deployed this new blackout to counter potential cyberattacks during their own military operation, but also to avoid leaking the locations of senior regime figures through metadata and user-generated content,» he said.
«Communications would have been limited, and Iran’s leadership would have proceeded with the assumption that all communications, including satellite or whitelisted networks, carry risks,» he said before claiming that «paranoia would be well grounded at this point, with the blackout a belated but direct response to that.»
«Those participating directly would already know to avoid technology that could betray their whereabouts,» Toker said.
«However, the metadata may well have played a part in determining that the meeting of regime leaders was being held at the Tehran compound, who was in attendance, and at what time.»
DID THEY GET HIM? KHAMENEI’S FATE REMAINS UNKNOWN AFTER ISRAEL-US STRIKE LEVELS HIS COMPOUND

In this handout image provided by the Office of the Supreme Leader of Iran, Iranian Supreme Leader Ali Khamenei addresses the nation in a state television broadcast on June 18, 2025 in Tehran, Iran. (Office of the Supreme Leader of Iran via Getty Images)
Toker revealed that the broader network around the regime leaders and around the compound wouldn’t have had the same strict restrictions.
«This kind of adjacent ‘background noise’ can be correlated against other intelligence sources to build an understanding of activity on the ground,» he added.
«Smartphones are a readily available, almost ‘free’ source of intelligence, and even when locked down, they eventually connect to international online services and generate insights that can be used to pinpoint regime figures,» Toker said.
CLICK HERE TO DOWNLOAD THE FOX NEWS APP
«In the aftermath of Saturday’s strike, this concern will have been high on the remaining Iranian leadership’s minds, especially if they didn’t have a clear and specific understanding of how the meeting was compromised.»
Iran has previously imposed sweeping internet shutdowns during periods of domestic unrest, including nationwide protests in January, which saw thousands killed, often seeking to curb the spread of information and restrict coordination.
war with iran,ali khamenei,bombings,middle east,terrorism
INTERNACIONAL
El Salvador registra más de 25,000 inmuebles inscritos en el primer bimestre de 2026 y mantiene dinamismo en la creación de empresas

En lo que va del año 2026, el Centro Nacional de Registros (CNR) reporta la inscripción de 25,381 inmuebles, una cifra que equivale a $720 millones, según datos oficiales difundidos por el director ejecutivo del CNR, Camilo Trigueros. Este comportamiento refleja la continuidad de una tendencia positiva que se consolidó en 2025, cuando se efectuaron 151,567 transferencias de dominio, generando un movimiento superior a $4,212 millones en el mercado inmobiliario salvadoreño. El incremento interanual en las transferencias de dominio alcanzó el 13%, impulsado tanto por la recuperación de zonas residenciales antes afectadas por la violencia, como por el renovado interés de inversionistas y ciudadanos residentes en el exterior.
Trigueros explicó en entrevista con el Noticiero Hechos, de Canal 12, que el proceso de transferencia de dominio responde principalmente a operaciones de compraventa, aunque también se registran casos de donaciones y herencias. Un estudio interno del CNR identificó que, en años recientes, las compraventas en colonias bajo control de pandillas eran prácticamente inexistentes debido a la falta de compradores y al temor de los propietarios a vender. Actualmente, tras mejoras en las condiciones de seguridad, estas zonas experimentan una reactivación del mercado inmobiliario, con participación de inversionistas nacionales, extranjeros y miembros de la diáspora salvadoreña.
El dinamismo del sector inmobiliario se suma al crecimiento sostenido de la actividad empresarial en el país. De acuerdo con datos publicados por Infobae el 4 de enero, El Salvador cerró 2025 con la creación de 8,373 nuevas empresas y más de 13,000 solicitudes de registro de marca, alcanzando cifras récord para la economía nacional. El crecimiento interanual en la conformación de nuevas empresas fue del 11%, mientras que las solicitudes de marca aumentaron un 18%, con especial énfasis en los sectores de gastronomía y comercio. Entre los factores que explican esta expansión se encuentran la digitalización de trámites, la simplificación de procesos y la implementación de figuras jurídicas más accesibles, como las Sociedades por Acciones Simplificadas (SAS).
El inicio de 2026 mantiene la tendencia al alza. Según datos oficiales, solo en enero se constituyeron cerca de 900 nuevas entidades, lo que proyecta que, de mantenerse el ritmo actual, El Salvador podría superar las 10,000 empresas creadas al finalizar el año. La digitalización de los servicios del CNR permite que el 70% de los usuarios obtenga respuesta a sus trámites en menos de 24 horas, lo que ha fortalecido la confianza de los inversionistas y emprendedores.
La recuperación del sector inmobiliario y el auge en la creación de empresas se explican, en parte, por la percepción de mayor seguridad, la estabilidad macroeconómica y el fortalecimiento institucional. De acuerdo con el balance presentado por Trigueros en medios radiales y televisivos, la mayoría de las nuevas empresas corresponden a sectores de servicios y comercio, con énfasis en pequeñas empresas familiares y emprendimientos gastronómicos. Además, la eliminación de barreras burocráticas y la gratuidad de trámites electrónicos han sido determinantes para el aumento de la formalización empresarial.
En 2025, la demanda de servicios del CNR creció un 11.1%, con más de 130,000 atenciones registradas a nivel nacional. El Instituto Adam Smith de la Universidad de la Florida ubicó a El Salvador en la quinta posición de facilidad para abrir una empresa en Latinoamérica, subiendo quince posiciones respecto a años previos. Las autoridades anticipan que la continuidad de las reformas y la ampliación de los servicios digitales mantendrán el ritmo de crecimiento en ambos rubros durante 2026.
corresponsal:Desde San Salvador, El Salvador

 CHIMENTOS2 días ago
CHIMENTOS2 días agoAlarma por la salud de Divina Gloria tras salir de Gran Hermano: “La internaron directamente en terapia intensiva”

 CHIMENTOS2 días ago
CHIMENTOS2 días agoGinette Reynal dio una rotunda marcha atrás con una decisión que tomó hace dos meses: “No aguanto más”

 CHIMENTOS2 días ago
CHIMENTOS2 días ago¡Titi revolucionó Gran Hermano! Cuáles son las 5 cosas que ya extraña: «Accesorios, pilates, bondiola, auriculares y bailar»





























